Theories:
SCRis a means of converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as NOxwith the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (N2) and water.The catalyst used is typically aqueous ammonia or urea.
(SCR=selective catalytic reduction)
Theories:
SCR is a means of converting nitrogenoxides, also referred to as NOx with the aid of a catalyst intodiatomic nitrogen (N2) and water. The catalyst used is typicallyaqueous ammonia or urea.
SCR is reduction of NOx underrelatively low temperature (300~450℃). A gaseousreductant is absorbed on the catalyst. NOx is removed when the fluegas passes through the catalyst chamber. SCR is shown to reduce NOxby at least 85%. As a mature NOx removing method, it is typicallyfound on power plants in China and abroad.
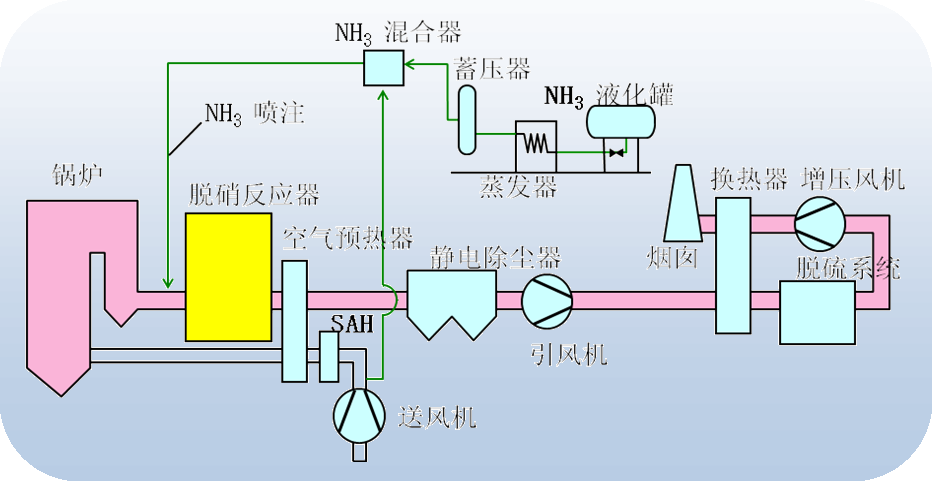
Process flow:
Boiler ammonia injection nozzles aqueous ammonia storage vaporizer pressure accumulator mixer SCR reduction module airheater forced draft fan ESP induced draft fan stack desulfurization booster fan
Formulas:
4NO+4NH3+O2=4N2+6H2O
2NO2+4NH3+O2=3N2+6H2O
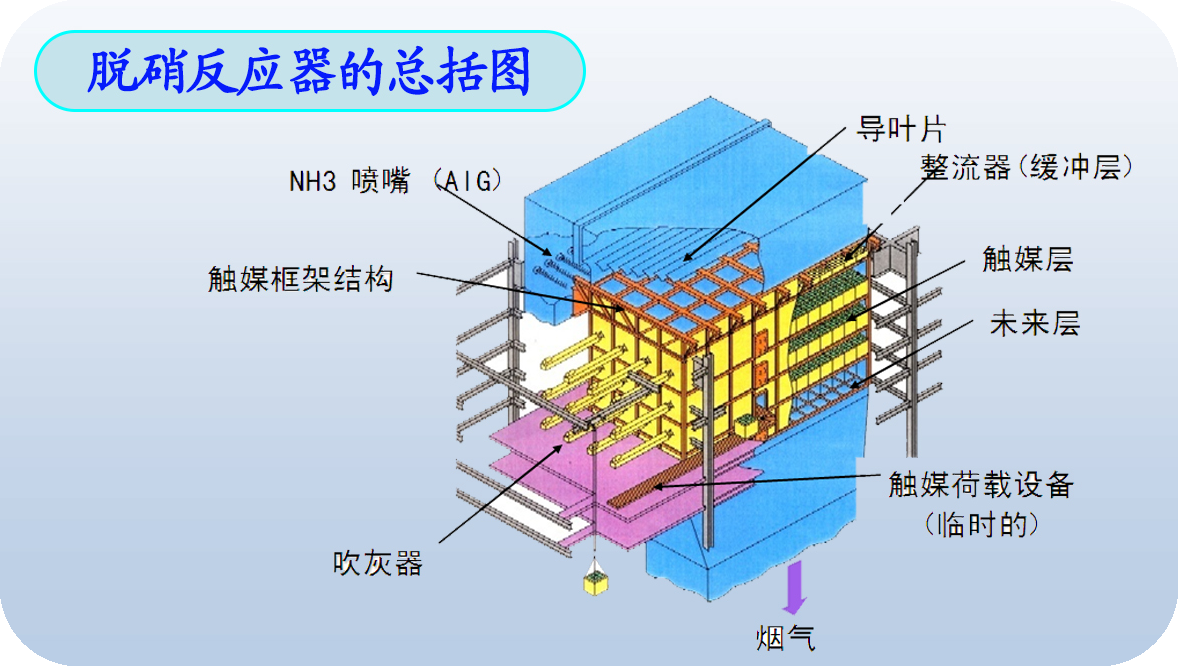
Features:
1.Complicatedstructure, but operates conveniently.
2.Fewmoving components, high reliability.
3.Noside reaction consuming catalyst.
4.HighNOx reduction: 80%~90%.
5.Highinvestment cost.
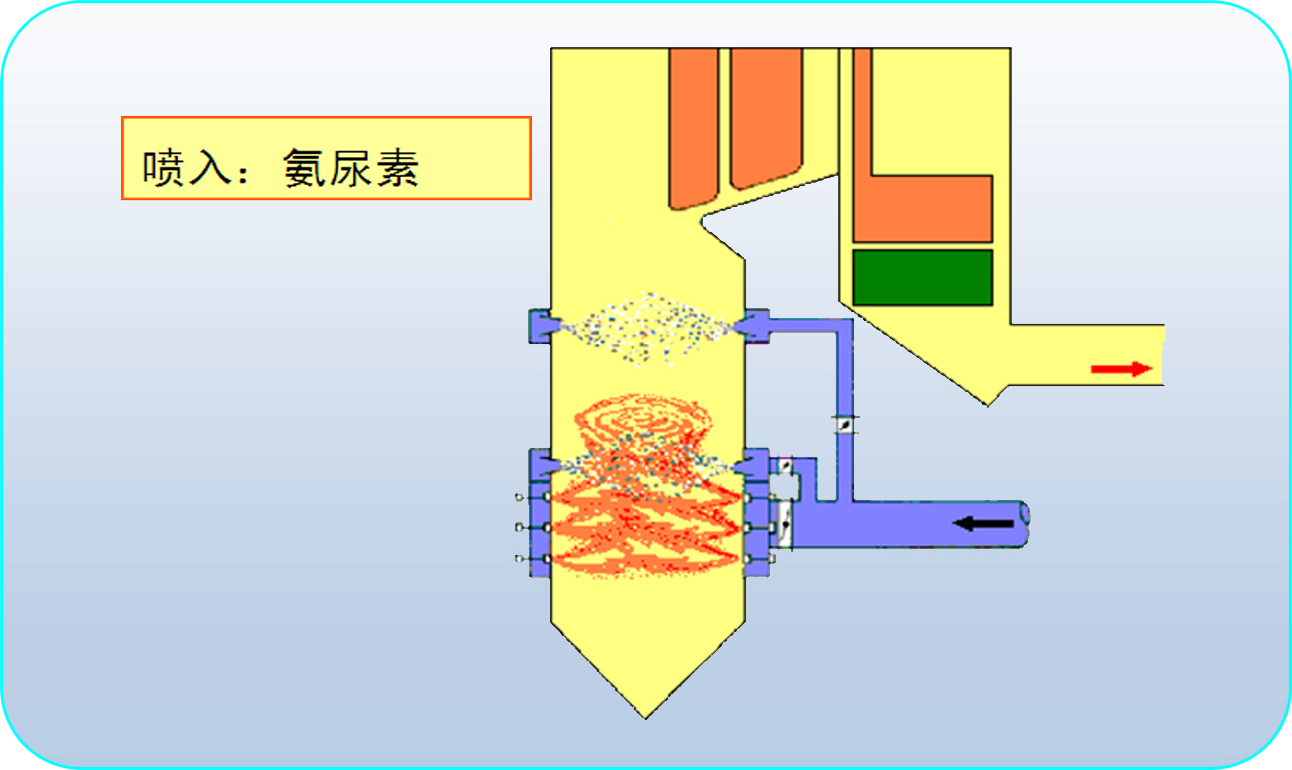
SNCR:
In SNCR, NH3 and urea areinjected into the boiler to react with NOx without catalyst.Therefore, reductant should be injected at the high temperature zone, where is850~1100℃. NH3 reacts rapidly with NOx to produce N2and H2O. The boiler is the reactor for this method.
Features:
1.Low total cost of ownership—investment& maintenance cost;
2.High-efficiency NOxremoval, 50-70%;
3.Take up small space;
4.No catalyst used;
5.to different coalcategory.
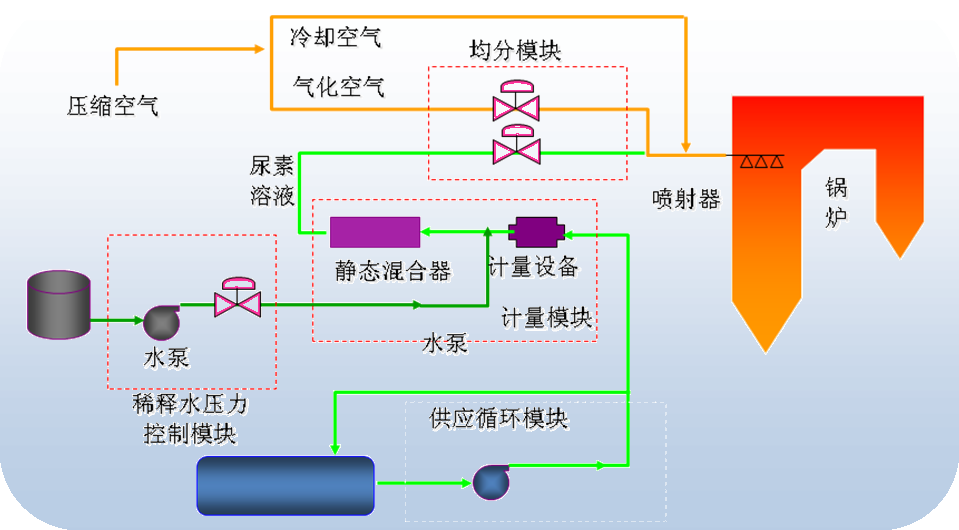
Process flow:
京ICP备05048247号 版权所有 开元体育(中国)制造有限公司 E-mail
